The vaginal ring is a popular contraceptive option for women. It offers a convenient and effective method of birth control. Understanding how the vaginal ring works, its benefits, potential side effects, and how to use it correctly are crucial for those considering this form of contraception.
In this article, we will delve into the definition and purpose of the vaginal ring, its components, mechanism of action, effectiveness, and efficiency. We will also explore the benefits, potential side effects, and risks associated with its use. Additionally, we will provide instructions on how to use the vaginal ring correctly and maintain it for optimal effectiveness.

Tóm tắt nội dung
- 1 Understanding the vaginal ring
- 2 How does a vaginal ring work?
- 3 Benefits of using the vaginal ring
- 4 Potential Vaginal Ring Side Effects and Risks
- 5 How to use the vaginal ring
- 6 FAQ
- 6.0.0.1 How effective is the vaginal ring in preventing pregnancy?
- 6.0.0.2 Is a prescription required to obtain a vaginal ring?
- 6.0.0.3 How is the vaginal ring inserted and removed?
- 6.0.0.4 Can the vaginal ring be felt or cause discomfort during intercourse?
- 6.0.0.5 Can the vaginal ring be used for purposes other than contraception?
- 6.0.0.6 How quickly does fertility return after discontinuing the vaginal ring?
- 6.0.0.7 Are there age restrictions for using the vaginal ring?
- 6.0.0.8 What should I do if the vaginal ring falls out or is expelled accidentally?
Understanding the vaginal ring
Definition and purpose of the Vaginal Ring
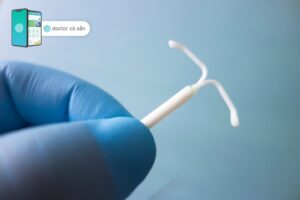
The vaginal ring, also known as the contraceptive ring, is a small, flexible, and transparent ring that is inserted into the vagina. Its main purpose is to prevent pregnancy by releasing hormones that inhibit ovulation (the release of an egg from the ovaries).
The vaginal ring is made of a combination of hormones, estrogen, and progestin. These hormones work together to suppress ovulation and alter the cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to reach an egg.
When inserted correctly, the vaginal ring provides a continuous and reliable method of contraception. It is an attractive option for many women due to its convenience and effectiveness.
Unlike other hormonal contraceptives, such as birth control pills, the vaginal ring only needs to be inserted once a month. This makes it a popular choice for women who may have difficulty remembering to take a daily pill.
Furthermore, the vaginal ring offers additional benefits beyond contraception. It can help regulate menstrual cycles, reduce menstrual cramps, and improve acne in some women.
Components of the Vaginal Ring
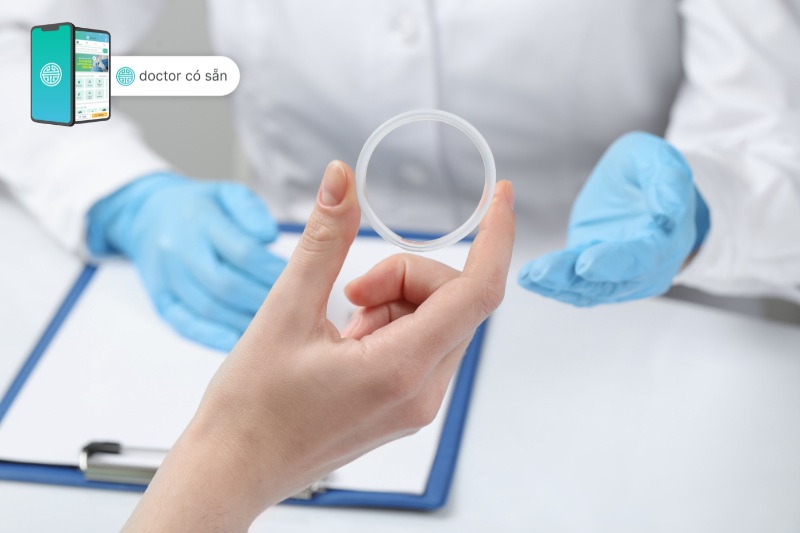
The vaginal ring consists of a flexible plastic ring that is about 2 inches in diameter. It is made of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer. This material ensures that the ring is safe, comfortable, and easily inserted and removed.

The inner part of the ring contains a combination of ethinyl estradiol and etonogestrel, which are synthetic versions of the hormones estrogen and progestin. These hormones are slowly released into the bloodstream through the vaginal walls.
It is important to note that the vaginal ring does not contain any latex, making it suitable for women with latex allergies. Additionally, the ring is odorless and does not interfere with sexual intercourse.
When inserted, the vaginal ring sits high up in the vagina, near the cervix. It is designed to stay in place during daily activities, including exercise, swimming, and showering. Most women do not feel the presence of the ring once it is properly positioned.
Each vaginal ring is individually packaged and comes with detailed instructions on how to insert and remove it. It is crucial to follow these instructions carefully to ensure optimal effectiveness and safety.
Overall, the vaginal ring offers a discreet and effective contraceptive option for women who prefer a non-daily method. Its ease of use and additional benefits make it a popular choice among women seeking reliable birth control.
Get a consultation to know more about the vaginal ring:
How does a vaginal ring work?
The vaginal ring is a convenient and effective method of contraception that provides continuous protection against pregnancy. Let’s dive deeper into how this innovative contraceptive works and explore its effectiveness and efficiency.
Mechanism of Action
Once inserted, the vaginal ring releases a continuous low dose of hormones. These hormones, namely estrogen and progestin, are absorbed through the vaginal walls and enter the bloodstream. Their primary function is to prevent pregnancy by suppressing ovulation, which means that the release of eggs from the ovaries is inhibited.
But that’s not all! The vaginal ring offers additional layers of protection. It thickens the cervical mucus, creating a barrier that makes it difficult for sperm to swim through and reach the egg. Furthermore, it changes the lining of the uterus, making it less receptive to implantation if fertilization does occur.
Effectiveness and efficiency
The vaginal ring is renowned for its high effectiveness when used correctly. In fact, it boasts an impressively low failure rate of less than 1% when used consistently and as directed. However, it is crucial to use the ring correctly to ensure optimal effectiveness.
One of the major advantages of the vaginal ring is its convenience. Unlike birth control pills that require daily administration, the ring only needs to be inserted once and provides protection for up to three weeks. After three weeks, it is removed for a ring-free week, during which a withdrawal bleeding, similar to a menstrual period, may occur. At the end of the ring-free week, a new ring is inserted to continue contraception.
It is important to note that while the vaginal ring is highly effective at preventing pregnancy, it does not protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs). To ensure comprehensive protection, it is recommended to use condoms or other barrier methods in addition to the vaginal ring.
Overall, the vaginal ring offers a reliable and convenient option for individuals seeking effective contraception. Its mechanism of action, coupled with its high effectiveness rate, makes it a popular choice among many women. Remember, if you have any questions or concerns about the vaginal ring, consult with your healthcare provider who can provide personalized guidance and support.
Find the best Ob-gyn clinics for a consultation:
Benefits of using the vaginal ring
Convenience and ease of use
The vaginal ring offers a convenient and hassle-free method of birth control. Once inserted, there is no need to worry about taking a pill every day. The ring remains in place for three weeks before needing to be replaced, making it a convenient option for busy individuals or those prone to forgetfulness.
Another advantage of the vaginal ring is that it does not interfere with sexual activity. It is discrete and comfortable, with most women reporting that they are unable to feel it during intercourse.
Health and hormonal benefits
In addition to preventing pregnancy, the vaginal ring offers several health benefits. The hormones released by the ring can help regulate menstrual cycles, reduce menstrual cramps, and decrease the risk of developing certain types of cancers, such as ovarian and endometrial cancer.
For individuals with acne, the hormones in the vaginal ring can also help clear up skin and reduce breakouts. It is important to note, however, that the vaginal ring may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with a history of certain medical conditions or risk factors that make hormonal contraception less advisable. It is always recommended to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable form of contraception for individual circumstances.
Find the best Ob-gyn clinics for a consultation:
Potential Vaginal Ring Side Effects and Risks
Common Vaginal Ring Side Effects
Like any form of hormonal contraception, the vaginal ring may cause some side effects. These can include breast tenderness, nausea, headaches, or changes in mood. Most women find that these side effects are mild and improve after the first few months of use. If vaginal ring side effects persist or become severe, it is important to consult a healthcare provider.
Serious Risks and Complications
While rare, there are potential serious risks and complications associated with the use of the vaginal ring. These can include blood clots, heart attacks, strokes, or an increased risk of certain types of cancers. It is important to discuss any personal or family history of these conditions with a healthcare provider before using the vaginal ring. They can help assess individual risk factors and determine the safest contraceptive method.
How to use the vaginal ring
Insertion and removal process
Using the vaginal ring is relatively simple, but it is essential to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer or healthcare provider. To insert the ring, the woman can choose a comfortable position, such as standing with one leg raised or lying down. The ring is folded and gently inserted into the vagina, similar to inserting a tampon. Once inside, it should be placed in the upper part of the vaginal canal, ensuring that it is secure and comfortable.
After three weeks of use, the vaginal ring should be removed. This is done by hooking a finger into the ring and gently pulling it out. It is important to note the date and time of removal to ensure proper replacement after the ring-free week.
Maintenance and replacement
During the ring-free week, a woman may experience withdrawal bleeding, similar to a menstrual period. It is important not to exceed the one-week break to maintain contraceptive protection. At the end of the ring-free week, a new ring should be inserted. It is advisable to set a reminder to ensure timely replacement and continuous protection against pregnancy.
If the ring is accidentally expelled or removed for more than three hours, additional contraception (such as condoms) should be used to prevent pregnancy. It is important to consult a healthcare provider for guidance in such situations.

FAQ
How effective is the vaginal ring in preventing pregnancy?
When used correctly, the vaginal ring is highly effective, with a 91-99% success rate. Effectiveness may vary based on individual adherence and other factors.
Is a prescription required to obtain a vaginal ring?
Yes, in most countries, a prescription from a healthcare provider is required to obtain a vaginal ring.
How is the vaginal ring inserted and removed?
The ring is typically inserted into the vagina and left in place for 21 days. It is then removed, followed by a 7-day break. After the break, a new ring is inserted.
Can the vaginal ring be felt or cause discomfort during intercourse?
Most women do not feel the vaginal ring once it’s inserted correctly, and it should not interfere with sexual activities.
Can the vaginal ring be used for purposes other than contraception?
In some cases, ob-gyn healthcare providers may prescribe the vaginal ring to manage specific medical conditions, such as irregular periods or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
How quickly does fertility return after discontinuing the vaginal ring?
Fertility can return soon after discontinuing the vaginal ring, but it varies from person to person. It’s advisable to discuss family planning with a healthcare provider.
Are there age restrictions for using the vaginal ring?
The vaginal ring can be used by women of reproductive age, but eligibility may depend on individual health factors. Your healthcare provider can help determine suitability.
What should I do if the vaginal ring falls out or is expelled accidentally?
If the ring is out of the vagina for less than 3 hours, you can rinse it with cool to lukewarm water and reinsert it. If it’s out for longer or repeatedly falls out, follow the specific instructions provided with your product or consult your healthcare provider.
The vaginal ring is an effective and convenient contraceptive option for women. It works by releasing hormones that prevent ovulation and alter cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to reach an egg.
The ring offers several benefits, such as ease of use, menstrual cycle regulation, and potential health benefits. However, like any contraception, it is essential to be aware of potential side effects and risks.
By following the correct insertion, removal, and replacement processes, women can use the vaginal ring safely and effectively. It is always recommended to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable form of contraception based on individual needs and medical history.