Physical medicine and rehabilitation, also known as physical therapy, is a branch of medicine. It plays an important role in the treatment of patients who are recovering from surgery, injury, or being treated for a disabling health condition. Physical therapy may also be necessary for any condition that affects the nerves, muscles, bones, or brain, and results in temporary or permanent disability. In the following article, Docosan will clarify how physical therapy and rehabilitation are typically performed.
Tóm tắt nội dung
Cases requiring physical therapy
Physical therapy can be beneficial for many conditions that cause pain or limit normal mobility. Below are some situations where medical rehabilitation is often necessary:
- Stroke (cerebral infarction): A stroke is a blockage or rupture of the blood supply to the brain. The most important aspect of stroke recovery is rehabilitation exercises, which can help patients return to daily activities, restore lost function, and prevent further damage.
- Spinal injuries: Neck and back injuries require early treatment for the best results. Physical therapy and rehabilitation can help limit further damage and shorten the recovery time.
- Pain: If you experience severe pain after an injury or surgery, or because of a nerve or muscle condition, physical therapy can help ease the pain and allow you to better control it.
- Other conditions: Joint conditions that cause pain, stiffness, and limitation of movement, such as ankylosing spondylitis, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout, can also be treated with physical therapy. This therapy can help ease pain, improve range of motion, and enable patients to practice using their joints without further damage.
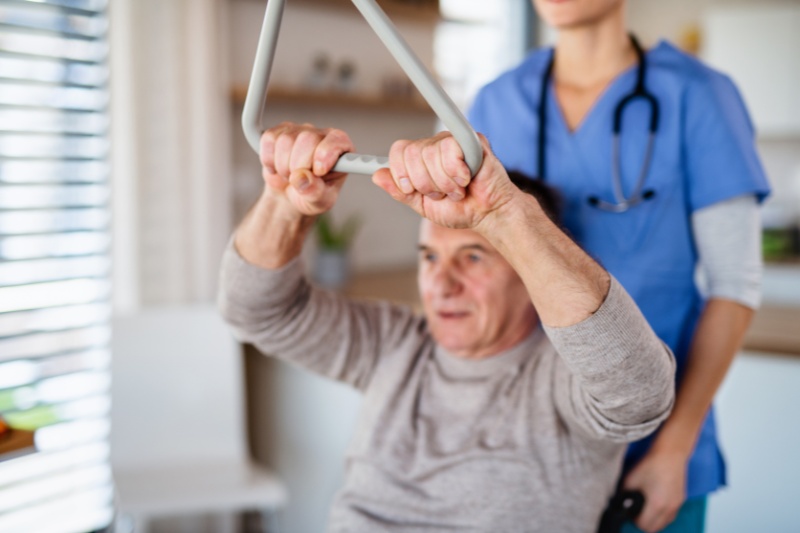

Additionally, patients may require physical rehabilitation for conditions such as cancer, heart disease, lung problems, infected wounds, amputations, or severe burns. Moreover, physical rehabilitation may also be necessary after joint replacement surgery.
Physical therapy and rehabilitation procedures
Initially, the physiotherapist will have a conversation with the patient, conduct an examination, order specific tests, and review medical records. Based on these findings, they will devise a personalized rehabilitative treatment plan that suits the patient’s individual needs. The physiotherapist will guide the patient through the process of implementing the rehabilitative treatment plan. They are highly trained in rehabilitation and physical movement after an injury or surgery.
Here are some ways in which physical therapists can assist patients:
- Help exercise and strengthen muscles.
- Assist in stretching muscles to increase flexibility.
- Provide a range of motion exercises to maintain or enhance motion.
- Offer exercises and activities to improve coordination and balance.
- Instruct patients on how to exercise on their own without a physiotherapist.
- Improve the healing process by using massage, heat, cold, electric current, or sound waves.
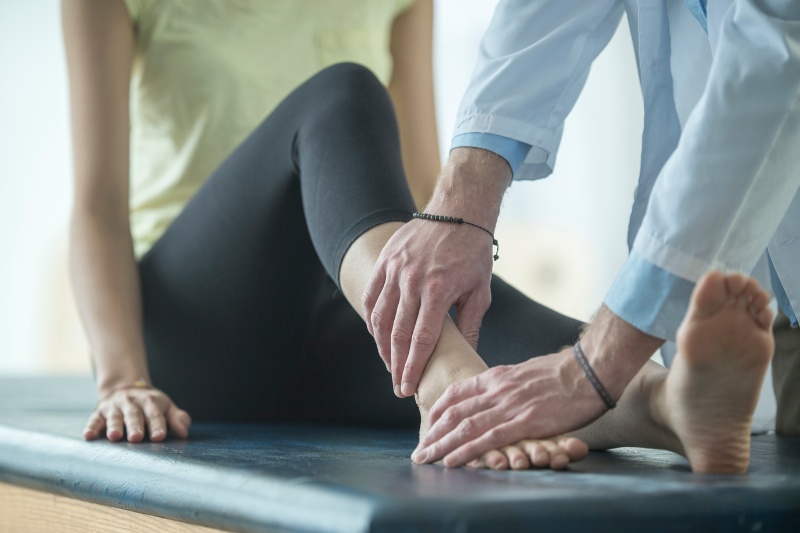

Rehabilitation physical therapy is a crucial aspect of the recovery process for many conditions. If a patient is admitted to a hospital, this often marks the beginning of a course of treatment that will continue even after the patient is discharged. The continuity of treatment can be maintained in an extended care facility, an outpatient physical therapy department, or even at home.
Patients can increase their chances of a successful recovery by gaining a thorough understanding of their condition and closely collaborating with physical therapists.
Prestigious doctor/rehabilitation clinic
- Dr. Nguyen Quy Hoang is one of the leading experts in musculoskeletal and rehabilitation medicine in Vietnam.
- Bonedoc is a rehabilitation center that has a team of experienced specialists and technicians.
- Phu Duc Traditional Medicine Clinic is one of the pioneers in deploying and developing the ‘Family Doctor’ medical model, with the scale of a ‘General Clinic’.
The article is consulted from doctors and reliable domestic and foreign sources.