A negative HIV test indicates that the person tested is not infected with the HIV virus. However, false negatives can occur due to inadequate testing time or incorrect procedures. So, what should you do when encountering true negative and false negative cases? Docosan will help answer this question in the article below.
Tóm tắt nội dung
What does a negative HIV test mean? Does it indicate that you are not infected with HIV?
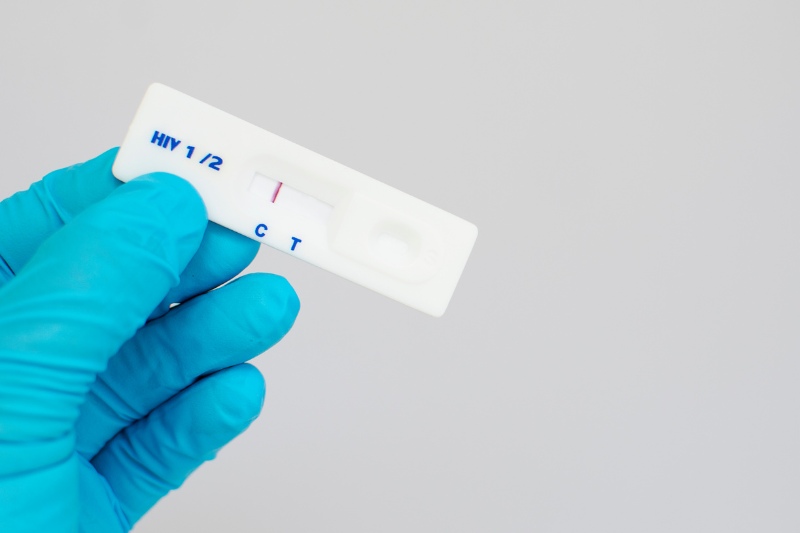
HIV testing is a specialized diagnostic method used for diagnosing and monitoring HIV treatment. Simply put, an HIV test checks whether a person is currently infected with HIV. Generally, the test results are either HIV positive or HIV negative.
- HIV negative: A negative result indicates that at the time of the test, the person taking the test did not carry the HIV virus or the test did not detect the virus in their body.
- HIV positive: In contrast, a positive result indicates that the HIV virus is present in the body. In this case, the person taking the test should promptly contact a doctor or an organization that specializes in HIV/AIDS for support.
What should I do if I get a negative HIV result?
HIV negative means that the person taking the test is not infected with HIV. However, if you are at high risk for HIV or are suspected of being infected, you need to follow:
Double check to get the most accurate result
Getting a negative HIV test result does not necessarily confirm that the person taking the test is not infected with HIV. False negative results can occur, especially during the window period when the viral load is not high enough to be detected by rapid testing. To ensure safety, it is important to get tested again after three months for the most accurate results.
Instead of testing at a hospital or clinic, you can choose the Docosan HIV/Syphilis Test Kit for convenient testing at home. This kit comes with a complete set of tools and detailed instructions for easy self-testing. After obtaining the test results, you will receive support to connect with a specialist for advice on treatment options and disease control measures, regardless of whether the result is HIV positive or negative.

See a health professional or doctor who specializes in HIV
Even if the second HIV test also yields negative or positive results, it is important to stay calm and seek help from a health professional or an HIV specialist as soon as possible, as this is good for your health.
Your doctor will discuss various issues with you to assess whether you are at risk of HIV infection. If you test positive for HIV, the doctor will order additional tests to determine how your immune system is functioning, what stage of the disease you are in, and your overall health status. After a thorough assessment, the doctor will develop a personalized treatment and control plan for your illness, and help you prevent infecting or spreading the disease to others.

Outline measures to prevent HIV infection
If your HIV test is negative, then congratulations, you are not infected with HIV. However, you need to map out the right HIV infection prevention measures so that you don’t have to worry:
- The best way to not get HIV is not to inject drugs.
- Practice a healthy sex life, do not have sex indiscriminately, be faithful to monogamy.
- If there is “stealth”, remember the condom. Because it’s an effective prevention measure to keep you from getting HIV, especially when having sex with someone you don’t know their exact health status.
- Blood transfusions and blood products should only be given when necessary.
- Do not share needles with others, must use sterile medical equipment.
- When it is known that the subject is infected with HIV, do not have direct contact with body fluids.
How long after exposure to HIV is an HIV test most accurate?
In order to obtain the most accurate confirmation of HIV infection, it is recommended to take an HIV test three months after being exposed to the virus (counting from the date of having sex, sharing needles, etc., with an infected person). At this point, a quick test kit can be used to check the results. However, if exposure is suspected or early signs of HIV are present, the test should be taken earlier, possibly around two months after exposure.
People at high risk of HIV should have periodic testing as recommended by their healthcare provider. This includes:
- Individuals who have unprotected sex with multiple partners
- Individuals who have sex with someone who has HIV
- Sex workers
- Men who have sex with men
- Individuals who have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection
- Individuals who share needles, medical equipment, or personal items that are prone to bleeding with HIV-infected people.

The early detection of HIV through testing helps doctors to plan appropriate treatment for each stage of the disease, as well as take necessary infection control measures.
A negative HIV test result indicates that no virus has been detected in the body. However, there is still a possibility of obtaining false negative results. The best course of action is to discuss this information with an HIV specialist to receive their advice, and to get retested after 3 months for the most accurate results.
The article is consulted from doctors and reliable domestic and foreign sources.